Dental Instruments: Names and Pictures ⎯ Article Plan
Exploring dental instruments, names, and pictures via readily available PDFs offers a comprehensive learning resource. Numerous websites, like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, provide visual guides.
Dental instruments represent a diverse array of specialized tools crucial for the practice of dentistry. Understanding their names, functions, and proper usage is paramount for dental professionals and students alike. Fortunately, a wealth of resources, including downloadable PDFs, are available to facilitate this learning process. Websites such as englishan.com and dishcuss.com offer visual guides showcasing various instruments.
These resources typically present instruments with clear pictures and corresponding names, aiding in quick identification. PDFs often categorize instruments based on their primary function – examination, cutting, restorative, or surgical – streamlining the learning experience. Accessing these PDFs allows for convenient offline study and reference. The images sourced from sites like englishan.com, with resolutions up to 1920×1080, provide detailed views essential for accurate identification. Mastering dental instrument nomenclature is the first step towards proficient dental care.
II. Basic Hand Instruments
Basic hand instruments form the foundation of many dental procedures, requiring manual dexterity and precise control. These tools, frequently depicted in dental instrument PDFs available online – resources highlighted on sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com – include explorers, probes, and various types of pliers. PDFs often categorize these instruments, providing labeled images for easy identification.
Understanding the subtle differences in design between instruments is crucial; for example, distinguishing between different types of forceps. High-resolution images, such as those found with dimensions up to 1920×1080, are invaluable for this purpose. These PDFs serve as excellent study aids, allowing students to visually learn and memorize the names and shapes of these essential tools; Proper identification, facilitated by these resources, is the first step towards skillful and safe application during clinical practice.
III. Examination Instruments
Examination instruments are vital for initial patient assessment, allowing dentists to gather crucial diagnostic information. Key tools, frequently illustrated in detailed dental instrument PDFs sourced from platforms like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, include the mouth mirror and dental explorer. These PDFs often present clear, labeled images, sometimes with dimensions reaching 1920×1080 pixels, aiding in accurate identification.
The mouth mirror, used for retraction and reflection, and the explorer, for detecting caries and irregularities, are foundational. Understanding their proper handling, as depicted in these visual guides, is paramount. These resources showcase the instruments’ shapes and functionalities, supporting effective learning. Accessing these PDFs provides a convenient and comprehensive way to familiarize oneself with the tools used to initiate a thorough dental examination and inform subsequent treatment planning.
III.a. Mouth Mirror
The mouth mirror, a fundamental examination tool, is frequently detailed in dental instrument PDFs available online, such as those found on englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These PDFs often feature high-resolution images – some reaching 1920×1080 pixels – clearly illustrating its circular reflective surface and attached handle. Its primary function is indirect vision, allowing dentists to view areas not directly visible.
Mouth mirrors also retract the tongue and cheeks, providing improved access and visibility. PDFs emphasize the importance of selecting the correct mirror size for patient comfort and effective examination. Different handle lengths and mirror head angles are often showcased. Studying these visual aids, readily accessible in PDF format, is crucial for dental students and professionals to master proper technique and instrument identification.
III.b. Dental Explorer
Dental explorers, essential for caries detection and assessing tooth morphology, are thoroughly documented in dental instrument PDFs sourced from sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These resources often present detailed images – some in webp format at resolutions like 1536×864 – showcasing the explorer’s pointed tip and angled shank. PDFs highlight the different types of explorers, including those with rounded or triangular tips.
Proper technique, as illustrated in these PDFs, involves using light pressure to feel for enamel irregularities or soft spots indicative of decay. The visual guides emphasize the importance of a systematic approach to avoid misdiagnosis. Understanding the explorer’s design and function, facilitated by these readily available PDFs, is vital for accurate clinical assessments and effective patient care.
IV. Cutting Instruments
Cutting instruments, crucial for tooth preparation and restorative procedures, are extensively illustrated in dental instrument PDFs available online. Resources like englishan.com and dishcuss.com provide visual references, often featuring images in JPG and webp formats (resolutions up to 1920×1080). These PDFs categorize cutting tools into scalers and curettes, detailing their specific designs and applications.
The PDFs emphasize the distinction between hand-operated and powered cutting instruments, such as ultrasonic scalers. Detailed diagrams showcase blade geometries and handle ergonomics. Understanding the proper selection and technique for each instrument, as presented in these visual guides, is paramount for precise and efficient dental work, minimizing trauma and maximizing treatment outcomes. Proper identification is key, as shown in the provided resources.
IV.a. Scalers
Dental scalers, essential for removing calculus and plaque, are thoroughly documented in downloadable PDFs. Websites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com offer visual guides, showcasing both hand scalers and ultrasonic varieties. These PDFs detail the different scaler tip shapes – sickle, triangular, and area-specific – alongside clear images (often in JPG or webp format, up to 1920×1080 resolution).
The resources highlight the importance of correct angulation and pressure when using scalers to avoid damaging tooth structure or soft tissues. PDFs often include diagrams illustrating proper scaling techniques. Ultrasonic scalers, powered by vibrations, are also explained, with attention given to tip selection and water coolant usage. These visual aids are invaluable for dental students and practitioners alike, ensuring accurate instrument identification and application.
IV.a.i. Hand Scalers
Hand scalers, fundamental tools for debridement, are extensively illustrated in dental instrument PDFs sourced from sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These resources showcase various types, including sickle scalers (for removing supragingival calculus) and Gracey curettes (often miscategorized, but used for subgingival scaling). PDFs provide detailed images – frequently in JPG or webp formats with resolutions up to 1920×1080 – highlighting the blade shapes and shank designs.
The downloadable guides emphasize proper grip, angulation, and stroke technique for effective calculus removal while minimizing trauma. They often include diagrams demonstrating the correct positioning for accessing different tooth surfaces. Understanding the specific purpose of each hand scaler, as detailed in these PDFs, is crucial for efficient and safe periodontal treatment. Visual learning aids are paramount for mastering their use.
IV.a.ii. Ultrasonic Scalers
Ultrasonic scalers, depicted in numerous dental instrument PDFs available online – notably from resources like englishan.com and dishcuss.com – represent a significant advancement in calculus removal. These PDFs showcase the different tip designs (slim, thick, Perio-Chip) and their specific applications for supragingival and subgingival scaling. Images, often in webp format with resolutions like 1536×864, illustrate the handpiece and its connection to the scaling unit.
The downloadable guides detail the mechanisms of action – cavitation, acoustic streaming, and mechanical action – and emphasize the importance of proper water coolant flow. They also address safety precautions, such as appropriate power settings and angulation to prevent damage to tooth structure. Understanding the nuances of ultrasonic scaling, as presented in these visual PDFs, is vital for modern dental hygiene practice.
IV.b. Curettes
Dental curettes, essential for subgingival scaling and root planing, are thoroughly illustrated in downloadable PDFs sourced from websites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These resources provide detailed images – often in JPG or webp formats with varying resolutions (e.g., 1920×1080, 1024×576) – showcasing the different blade designs and shank configurations. PDFs clarify distinctions between universal and area-specific curettes, highlighting Gracey, Barnes, and Michigan curettes.
Visual guides emphasize proper angulation and adaptation to the tooth surface for effective calculus removal. They also explain the importance of identifying anatomical landmarks to avoid tissue damage. These PDFs serve as valuable references for dental professionals, aiding in accurate instrument selection and technique, ensuring optimal periodontal health outcomes. Understanding these tools is crucial, as demonstrated in the provided resources.
IV.b.i. Universal Curettes
Universal curettes, characterized by a triangular cross-section, are versatile instruments for scaling supra- and subgingival calculus on all tooth surfaces. PDFs available on platforms like englishan.com and dishcuss.com visually demonstrate their design, often featuring images in formats like JPG and webp (resolutions ranging from 1920×1080 to 1024×576). These resources highlight the rounded toe and back, enabling adaptation to various tooth curvatures.
The downloadable guides illustrate proper grip, angulation, and stroke techniques for effective calculus removal. They emphasize the importance of a pull stroke approach. PDFs clarify how universal curettes differ from area-specific designs, focusing on their adaptability. These visual aids are invaluable for dental students and practitioners, promoting correct instrument handling and minimizing tissue trauma, as depicted in the provided online materials.
IV.b.ii. Area-Specific Curettes
Area-specific curettes, unlike their universal counterparts, are designed for dedicated use on anterior teeth – typically Gracey curettes for anterior surfaces and modified Gracey curettes for posterior regions. PDFs sourced from sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com showcase these instruments, often in JPG and webp formats (varying from 1920×1080 down to 1024×576 resolution). These visual guides detail the blade’s offset and unique cross-sectional shape.
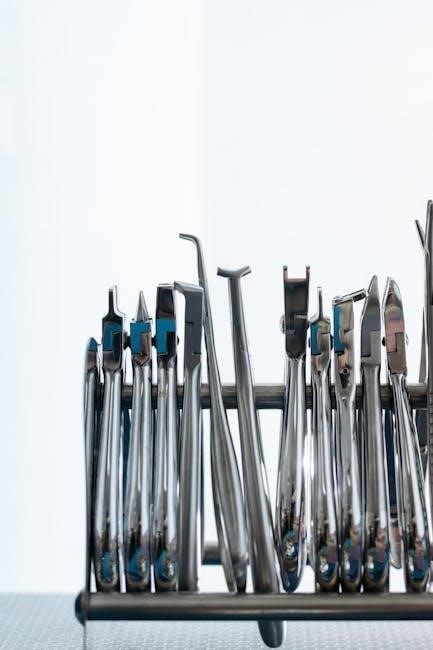
The downloadable resources emphasize the importance of selecting the correct curette for the specific tooth surface to maximize efficiency and minimize discomfort. They illustrate how the blade’s adaptation differs based on tooth anatomy. PDFs clarify the numbering system for Gracey curettes, linking each number to a specific area. These visual aids are crucial for mastering periodontal scaling techniques, ensuring effective calculus removal and promoting optimal patient care, as demonstrated in the online materials.
V. Restorative Instruments
Restorative dentistry relies on specialized instruments for procedures like fillings and reconstructions. PDFs available online, referencing sources like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, visually depict key tools. These resources, often presented in JPG and webp formats (resolutions ranging from 1920×1080 to 1024×576), highlight instruments like amalgam carriers and condensers.
Amalgam carriers efficiently transport and condense amalgam alloy into prepared cavities. Condensers, conversely, compact the restorative material, ensuring a dense and durable restoration. The downloadable PDFs detail the shapes and sizes of these instruments, emphasizing their specific functions. They also illustrate proper handling techniques for optimal results. Understanding these tools, as shown in the images, is vital for successful restorative treatments and long-lasting dental work, as demonstrated by the online visual guides.
V.a. Amalgam Carriers
Amalgam carriers are essential restorative instruments used to precisely transport and deliver amalgam alloy into tooth cavities. Online resources, including PDFs sourced from sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, provide detailed visual representations – often in JPG or webp formats with varying resolutions (e.g., 1920×1080, 1536×864). These images showcase the carrier’s typical design: a handle connected to a replaceable capsule.
PDF guides illustrate how to load the capsule with the correct proportion of alloy and mercury. They also demonstrate the technique for condensing the amalgam within the prepared tooth structure. Proper use, as depicted in the downloadable materials, minimizes waste and ensures optimal adaptation of the restorative material; Understanding the carrier’s components and function, through these visual aids, is crucial for efficient and effective amalgam restorations.
V.b. Condensers
Dental condensers are vital instruments for compacting restorative materials, primarily amalgam, within a tooth preparation. Numerous PDFs, accessible through websites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, offer clear images – often in webp or JPG format (resolutions ranging from 1024×576 to 1920×1080) – illustrating various condenser types. These include straight, tapered, and ball-ended condensers.
These downloadable resources demonstrate the proper technique for condensing amalgam in incremental layers, ensuring complete adaptation to the cavity walls and minimizing voids. The PDFs highlight the importance of applying firm, controlled pressure. Visual guides showcase how different condenser tips are used for specific areas of the preparation. Mastering condensation, as illustrated in these materials, is essential for creating durable and long-lasting amalgam restorations, preventing marginal breakdown and secondary caries.
VI. Rotary Instruments
Rotary instruments, crucial for cutting, shaping, and polishing dental tissues, are extensively documented in downloadable PDFs found on platforms like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These resources showcase a diverse range of burs and mandrels, often presented in high-resolution images (webp and jpg formats, up to 1920×1080). PDFs detail the distinctions between Tungsten Carbide and Diamond burs, highlighting their specific applications.
Tungsten Carbide burs excel in cutting enamel and composite, while Diamond burs are ideal for harder tissues like porcelain and enamel. Mandrels, essential for securing burs, are also visually represented. These PDFs often include charts detailing bur shapes, sizes, and grit types, aiding in proper selection. Understanding these instruments, as presented in these visual guides, is fundamental for efficient and precise dental procedures.
VI.a. Dental Burs
Dental burs, essential rotary cutting tools, are comprehensively illustrated in PDFs available online, notably through resources like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These downloadable guides present burs in various formats – jpg and webp, with resolutions reaching 1920×1080 – enabling detailed visual identification. PDFs categorize burs based on their cutting efficiency and material composition.
A key distinction highlighted in these resources is between Tungsten Carbide and Diamond burs. Tungsten Carbide burs are favored for their strength and efficiency on restorative materials, while Diamond burs excel in precision cutting of enamel and porcelain. The PDFs often include detailed charts specifying bur shapes (round, pear, cone) and grit sizes, crucial for selecting the appropriate bur for each clinical application. Visual learning aids significantly enhance understanding.
VI.a.i. Tungsten Carbide Burs
Tungsten Carbide burs, frequently depicted in dental instrument PDFs sourced from sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, are known for their robust cutting ability and durability. These PDFs, often available in jpg and webp formats (resolutions up to 1920×1080), showcase a diverse range of shapes – round, pear, cone, and inverted cone – each designed for specific dental procedures.
The downloadable guides emphasize that Tungsten Carbide burs are ideal for removing caries from dentin and preparing cavities in composite restorations. They are less prone to chipping compared to diamond burs, making them a reliable choice for general dentistry. PDFs often include detailed illustrations demonstrating the correct bur selection based on tooth structure and restorative material. Understanding these visual guides is crucial for effective use.
VI.a.ii. Diamond Burs
Diamond burs, prominently featured in dental instrument identification PDFs from resources like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, are renowned for their precision and versatility. These PDFs, often presented in formats like jpg and webp with resolutions reaching 1920×1080, illustrate a wide array of diamond bur shapes – including fine, medium, and coarse grits – catering to diverse clinical needs.
The downloadable guides highlight that diamond burs excel in enamel cutting, crown preparation, and porcelain adjustments. Their abrasive nature allows for efficient material removal, but requires careful technique to prevent overheating. Visual aids within the PDFs demonstrate proper bur angulation and speed control. These resources are invaluable for dental students and practitioners seeking to refine their restorative techniques and instrument knowledge.

VI.b. Mandrels
Dental mandrels, essential components alongside burs as depicted in dental instrument PDFs sourced from sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, serve as the crucial link between the rotary handpiece and the bur. These PDFs, often available in jpg and webp formats with varying resolutions (e.g., 1920×1080, 1536×864), clearly illustrate different mandrel shank types – latch-type and friction-grip – and their corresponding handpiece compatibility.
The visual guides emphasize the importance of selecting the correct mandrel size to securely hold the bur, preventing slippage during procedures. Proper mandrel use ensures efficient cutting and minimizes the risk of instrument fracture. Detailed images within these downloadable resources showcase the mandrel’s chuck mechanism and demonstrate correct bur insertion and tightening techniques, aiding in safe and effective operation.
VII. Surgical Instruments
Dental surgical instruments, comprehensively illustrated in PDFs available online – notably through resources like englishan.com and dishcuss.com – are vital for oral surgical procedures. These downloadable guides, often presented as high-resolution jpg and webp images (ranging from 1920×1080 to 1024×576), showcase instruments like periosteal elevators and bone files.
The PDFs detail the specific uses of each instrument; periosteal elevators gently separate the periosteum from the bone, while bone files refine bone shapes. Visual aids demonstrate proper handling techniques, emphasizing safety and precision. These resources are invaluable for dental students and practitioners seeking to identify and understand the function of each surgical tool, ensuring optimal patient care and procedural success.
VII.a. Periosteal Elevator

Periosteal elevators, clearly depicted in dental instrument PDFs sourced from sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, are essential for surgical procedures. These visual guides, often in jpg or webp format (resolutions varying from 1920×1080 down to 1024×576), illustrate the instrument’s design – typically a curved blade attached to a handle.
PDF resources detail how periosteal elevators are used to carefully separate the periosteum from the underlying bone, creating a flap for access during surgical interventions. The images showcase different elevator types, highlighting variations in blade shape and size. Understanding the proper technique, as demonstrated in these PDFs, is crucial for minimizing trauma and ensuring successful flap elevation during oral surgery.
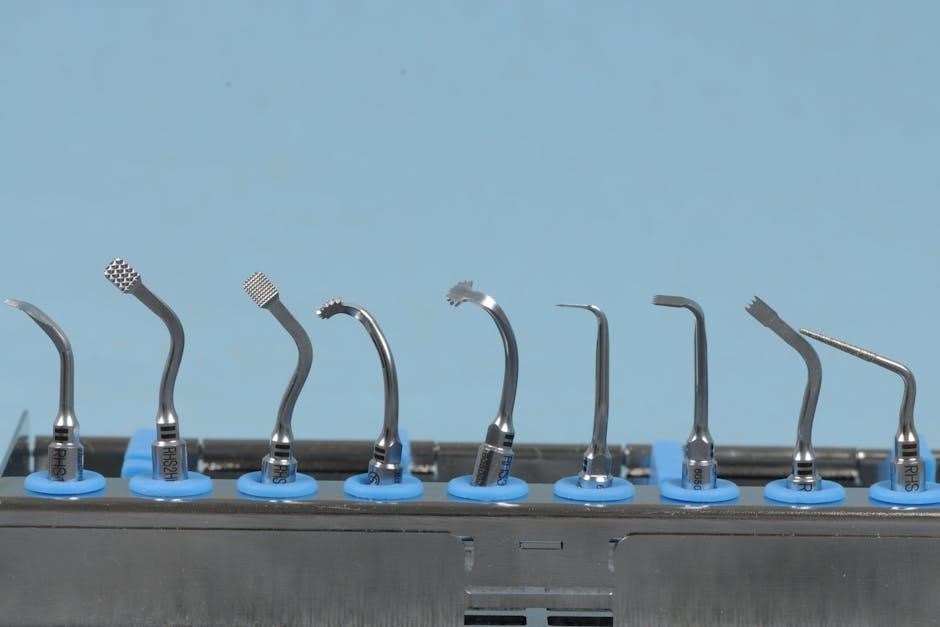
VII.b. Bone File
Bone files, frequently visualized in dental instrument PDFs available on platforms like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, are utilized for shaping and smoothing bone during surgical procedures. These PDFs, often presenting images in formats like jpg and webp (with resolutions ranging from 1920×1080 to 1024×576), clearly demonstrate the instrument’s characteristic rough surface.
The downloadable resources illustrate how bone files are employed to refine bone contours, remove sharp edges, and create precise bony adjustments. Different file designs – varying in coarseness and shape – are showcased, aiding in selecting the appropriate tool for specific surgical tasks. Proper usage, as detailed in these PDFs, is vital to avoid excessive bone removal and maintain surgical precision during oral and maxillofacial surgeries.
VIII. Impression Materials & Instruments
Impression materials and instruments are visually detailed in numerous dental instrument PDFs sourced from websites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These resources, often presenting images in jpg and webp formats (resolutions varying from 1920×1080 down to 1024×576), showcase the tools used to capture accurate dental impressions.
PDFs illustrate impression trays – stock and custom-made – alongside materials like alginate, silicone, and polyether. Instruments like mixing pads, spatulas, and impression guns are also clearly depicted. These downloadable guides emphasize the importance of proper material handling and tray selection for optimal impression accuracy. Understanding these tools, as presented in these visual resources, is crucial for restorative dentistry and prosthodontics, ensuring well-fitting dental restorations.
IX. Instruments for Endodontic Treatment
Endodontic instruments, essential for root canal procedures, are thoroughly documented in dental instrument PDFs available online, notably through resources like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These PDFs, featuring images in formats like jpg and webp (ranging from 1920×1080 to smaller resolutions), visually detail the specialized tools required for successful endodontic therapy.
Key instruments illustrated include files (K-files, H-files, and rotary files), reamers, spreaders, and pluggers. PDFs also showcase apex locators and intra-canal irrigation syringes. Visual guides emphasize proper instrument selection, sequence of use, and techniques for effective canal shaping and obturation. These resources are invaluable for dental students and practitioners seeking a comprehensive understanding of endodontic instrumentation, ensuring precise and effective root canal treatment.
X. Instruments for Periodontal Treatment
Periodontal instruments, crucial for managing gum disease, are extensively illustrated in downloadable PDFs sourced from websites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These resources present detailed images – often in jpg and webp formats with varying resolutions (up to 1920×1080) – of the tools used in scaling, root planing, and periodontal surgery.
PDFs showcase a range of instruments, including scalers (hand and ultrasonic), curettes (universal and area-specific), periodontal probes, and gingival chisels. They also depict instruments for flap procedures, such as periosteal elevators and bone files. These visual guides clarify instrument design, angulation, and proper technique for effective subgingival debridement and tissue management, aiding in the treatment and prevention of periodontal disease.
XI. Instruments for Orthodontic Treatment
Orthodontic instruments, essential for teeth alignment, are visually detailed in PDFs available online, including resources referenced on englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These downloadable guides present clear pictures – often in webp and jpg formats, with resolutions ranging up to 1920×1080 – of the tools used in bracket placement, wire bending, and archwire adjustments.
PDFs illustrate instruments like bracket tweezers, ligature cutters, contouring pliers, and archwire formers. They also showcase instruments for indirect bonding and surgical orthodontics. These visual aids clarify instrument function and proper handling, crucial for precise tooth movement and achieving optimal orthodontic results. Understanding these tools, through detailed images, is vital for effective orthodontic treatment planning and execution.
XII. Digital Dental Instruments
Digital dentistry increasingly incorporates advanced instruments, often showcased in comprehensive PDF guides sourced from platforms like englishan.com and dishcuss.com. These resources depict intraoral scanners, digital impression systems, and CAD/CAM milling machines, presenting clear visuals of their components and operation. Images, frequently in webp or jpg format with resolutions up to 1920×1080, illustrate the technology’s precision.
PDFs detail digital radiography sensors, transillumination devices, and laser scanners used for diagnostics and treatment planning. They also cover software interfaces for design and simulation. Understanding these digital tools, through detailed pictures, is crucial for modern dental practice. These visual aids enhance comprehension of workflows and optimize treatment outcomes, representing a significant shift in dental technology.
XIII. Sterilization and Maintenance of Instruments
Maintaining sterility is paramount in dentistry, and detailed PDFs, often found on sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com, visually demonstrate proper procedures. These guides showcase autoclaves, ultrasonic cleaners, and chemical sterilization solutions, alongside images of instrument cassettes and packaging materials. Pictures illustrate correct instrument sorting, cleaning, and lubrication techniques, crucial for longevity.
PDF resources emphasize the importance of regular maintenance, including sharpening, oiling, and inspection for corrosion or damage. Visual aids depict identifying worn or broken instruments, preventing cross-contamination, and adhering to infection control protocols. Understanding these processes, supported by clear images, ensures patient safety and instrument effectiveness, extending their lifespan and upholding professional standards.
XIV. Resources for Dental Instrument Identification (PDFs)
Numerous online resources offer downloadable PDFs dedicated to dental instrument identification, with sites like englishan.com and dishcuss.com being valuable starting points. These PDFs typically feature high-resolution images paired with detailed instrument names and descriptions, aiding in accurate recognition. They often categorize instruments by function – basic, restorative, surgical, or endodontic – simplifying the learning process.
Many PDFs include quizzes or interactive elements to test knowledge, reinforcing identification skills. Some resources focus on specific brands or instrument sets, while others provide comprehensive overviews. Utilizing these visual guides, often available for free, is crucial for dental students, assistants, and hygienists to confidently identify and utilize the correct tools, ensuring efficient and safe patient care.